International
International collaborations & interdisciplinary actions all around the world :

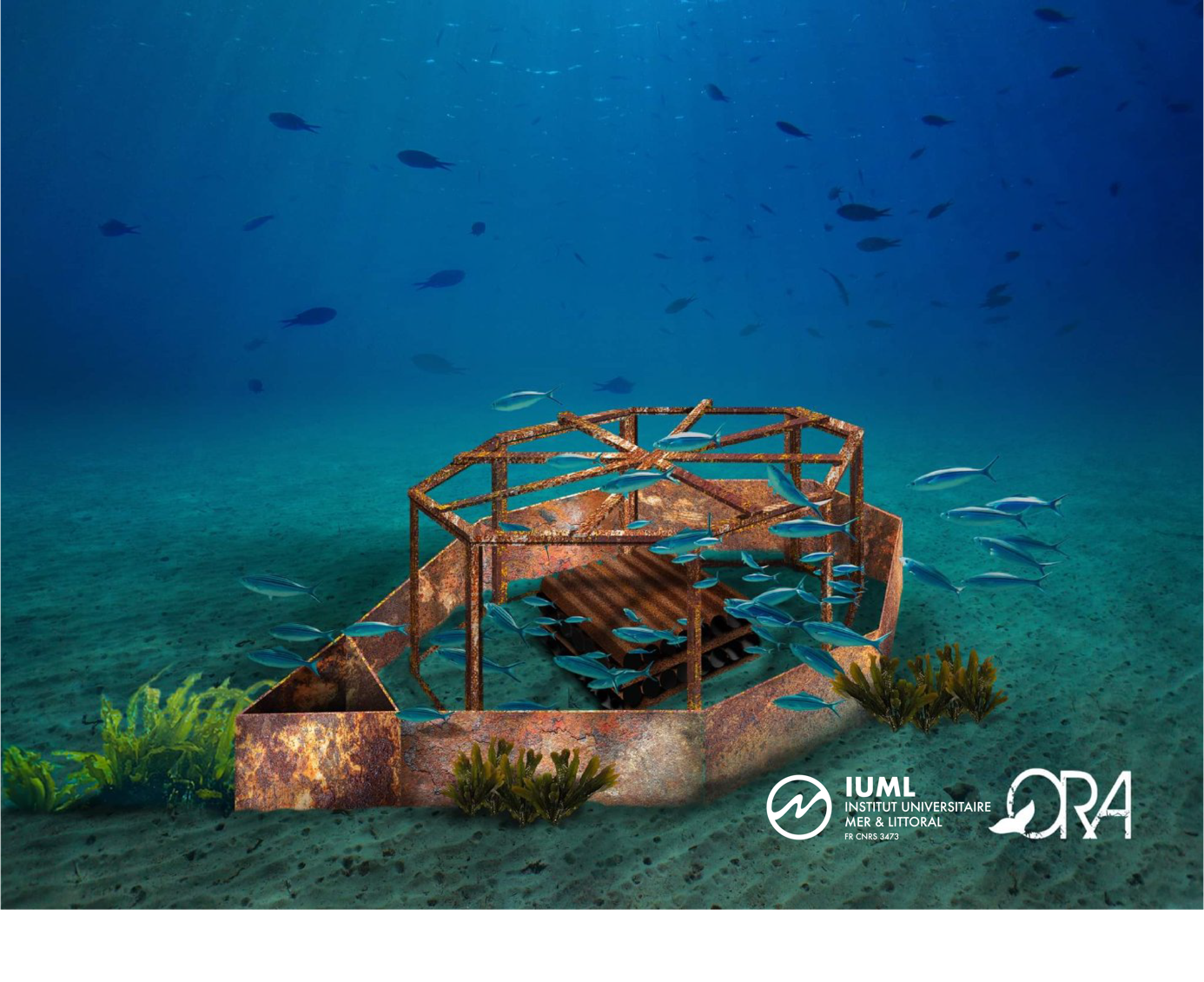
INP-HB 's laboratory in collaboration with IUML & Capacités 
Created thanks to the Fonds de Soutien aux Actions de Coopération Internationale of the Region of Pays de la Loire, and with the participation of Capacités, this laboratory aims to simulate the conditions of life of structures in marine environment. This laboratory is a sister facility to the GeM (Institut de Recherche en Génie Civil et Mécanique), a joint research unit of Nantes University, Centrale Nantes and the CNRS. The installation of this laboratory will allow tests to be carried out as close as possible to the conditions of Côte d'Ivoire and to adapt to them. It is therefore a monitoring of structures and civil engineering works in the marine environment that has been installed in Yamoussoukro. The latter will be subjected to the various mechanical constraints of use and environmental constraints, the concrete structures, among others, may be damaged over time. In order to prevent these risks, monitoring allows us to identify and to understand the pathologies of materials, but also to monitor the structures thanks to fine instrumentation coupled with artificial intelligence algorithms. The objective is to reduce the maintenance costs of port and offshore concrete structures and to test sensors to study the aging of materials in the marine environment. Since, this project is a maritime interdisciplinary object (biofouling, material, sensors), it obtained a support from the IUML. After a presentation and an illustration of use by Magda Torres, the laboratory was inaugurated and the ribbon cut!For this first event, Cédric Fofana, graduate of the Marine Technology master, had the chance to test the equipment with Magda Torres, engineer at Capacités. Indeed, Cédric has been selected to continue his studies with a thesis at the INP-HB. His work will be based on experiments performed in the new laboratory.

Conducted by : Nantes University, Universty of Massachussetts Amherst, Colby College
Others partners : l’IUML: ISOMER, GeM, LEMNA BIOMOOR (UMass Nantes U, NREL)
Co-financed : WEAMEC (Région Pays de la Loire), Europe (FEDER), F. Russell Cole Student Research Fellows grant in Environmental Studies et Buck Lab for Climate and Environment au Colby College, Ocean Ressource and renewable Energy at the University of Massachusetts.

Marine energy technologies - offshore wind and oceanic wind - are among the five renewable energy technologies identified as priorities in the global strategic energy plans. Wind energy is expected to make the largest contribution to renewable energy goals. Its deployment at sea will be further expanded by the development of new wind energy systems, which can be installed in deeper waters (>50 m) and further offshore (up to 50 km): about 80% of offshore wind resources are in waters deeper than 60 meters. Social acceptability rests on two main pillars: the cost of energy and the integration of offshore structures in their environment, including land use planning. The I2FLOW (Improve the Environmental Integration of Floating Offshore Wind Turbines) project addresses these issues by optimizing the design of offshore structures and improving their acceptability in three ways:
- first by optimizing the design and integration of "artificial reefs" for local fish species at the offshore wind turbine anchor (developed by CETEAL) to naturally reduce the amount of biocolonization, thus the amount of material needed to ensure the reliability of the structure;
- second by analyzing the social acceptability by local communities (residents, fishermen, environmental protection associations). The sociological survey was prepared in 2021-2022 and tested during the event "Partez voir la Mer en 2022". Currently, the artificial reef and anchor coupons are being prepared for installation in spring 2023.
- The work on bio-colonization began with very original tests in the USA on wind turbine mooring chains with a 3D printed colonization.
Multi-Frame (2020 -2023) : Assessment Framework for successful development of viable ocean multi-use systems
Project financed by the ANR
French Managers : Josselin Guyot-Téphany & Brice Trouillet, Nantes Université, LETG
The ambition of the Multi-Frame project is to develop knowledge, both theoretical and practical, on the potential of multi-use at sea in a global perspective. It is part of a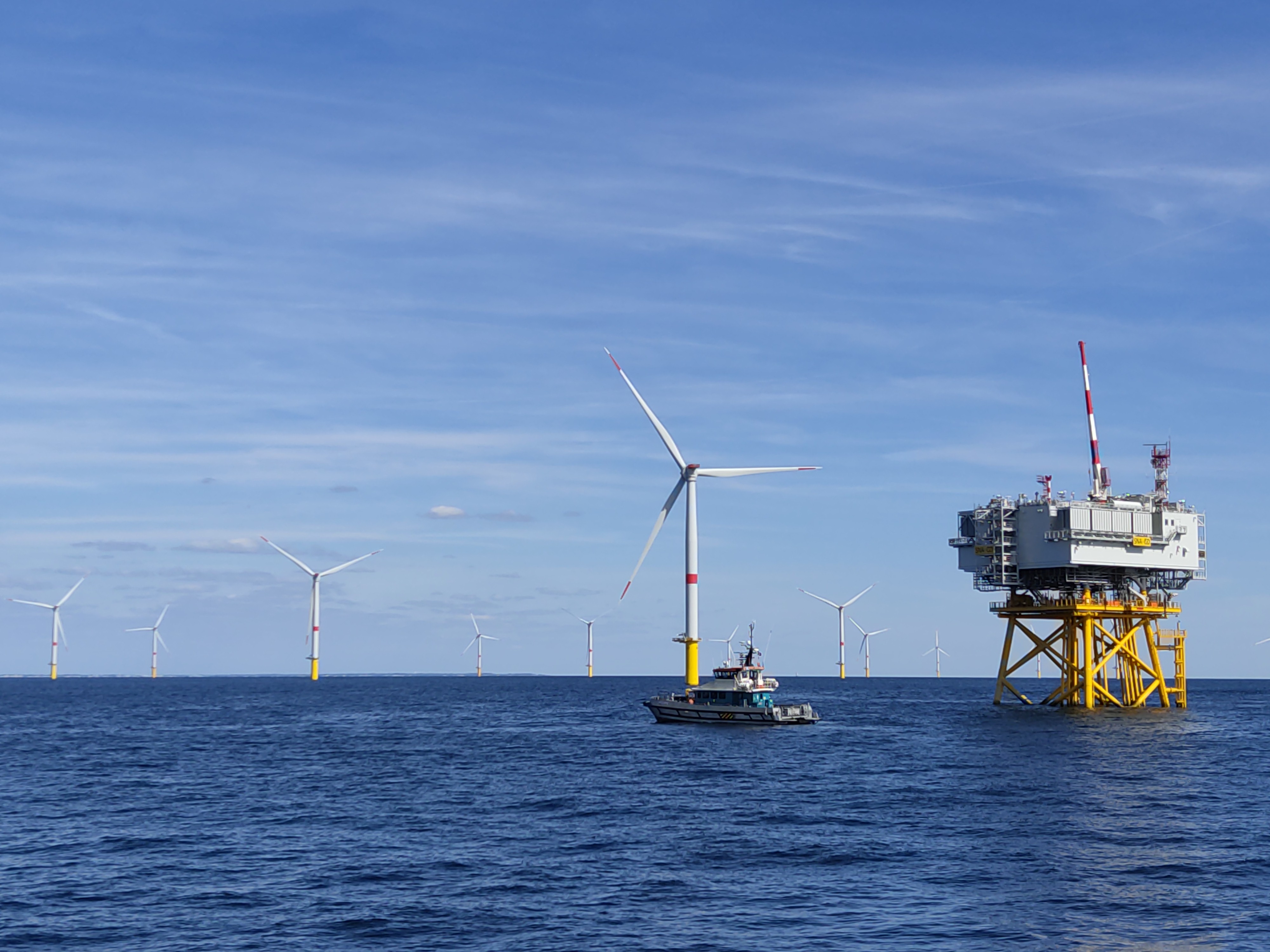 
French American Innovation Days from 2019 & 2022 
The French American Innovation Day gather experts from France and the United States (scientistes, entrepreneurs,...) about one specific subject in the field of Innovation. FAID is an annual Franco-American event which brings together scientists, companies, entrepreneurs and investors. It is a high-level event where researchers and companies have the opportunity to exchange views on a specific technological issue, start co-operative activities and develop business transactions with a transatlantic perspective. The goal of the program is to facilitate the development of innovation ties between France and America.
I am Antoine Dubois, a PhD student in Ecology and Marine Biology working for the ISOMer laboratory of Nantes University and supported by the IUML.
My thesis subject has the particularity of being multi-disciplinary with a part of my field (biology & ecology) and a sociological part. The aim of this subject is to understand the effect of increasing marine biodiversity (such as fish or invertebrates) on the biocolonization of different materials used in the offshore wind industry.We would like to apply the artificial reef concept to this field. The latter is the one tested in the sociological part of the project. To carry out this part, not being from the field, I am doing it, among others, with Alison Bates, a professor in environmental studies already familiar with sociological investigations.
I went to Colby College in Waterville (Maine, USA) for two weeks on international mobility to work directly on interviews conducted in coastal towns in the state, and also to conduct interviews with locals myself. We asked them about their opinions on offshore wind turbines and the concept of artificial reefs. Upon my return to France, I was able to conduct interviews in St Jean-de-Monts following the same protocol in order to get the opinions of French locals from the Pays-de-la-Loire region. At this time, I have not yet finished analyzing the data collected.
However, it was very interesting to see the number of similarities in the concerns and priorities of both French and American locals on the subject of floating and installed offshore wind farms. This mobility allowed me to focus entirely on the sociological part. Thus the implementation of an international survey (comparison between France and the USA) could start to be elaborated.
For the little anecdote, I had the opportunity to go with a group of students on an island (Vinalhaven) to visit an onshore wind farm. I was particularly impressed by the scenery and the lobster fishing culture there.

Project reference : H2020-SwafS-2018-1
The project concluded in December 2022 and it has overseen creation of 18 to 30 interventions related to gender equality (also, equality, diversity and inclusion), science communication and education, ethics and research integrity, open access, and public engagement in four research performing organisations (RPO) and one dual-function RPO and research funding organisation (RFO) in the marine and maritime sector. This has been achieved with the help of seven RRI expert partners in the GRRIP consortium. Representatives of the Quadruple Helix (higher educational institutes, private sector, government, and civil society) have been engaged in this project at various stages and in different research and innovation aspects.
4 examples of projects :
PLOCAN

The Oceanic Platform of the Canary Islands (PLOCAN) is a singular scientific and technological infrastructure (ICTS) aimed to accelerate the development of knowledge and technologies for the responsible and sustainable use of the ocean, in line with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and strategy of Blue Growth Strategy established by the European Union.
The main aim of the PLOCAN consortium is the construction and operation of a fixed offshore platform that will underpin national research and technological development capacities at the cutting edge of knowledge and within the framework of international competitiveness. The platform will be located both close to the coast and near the edge of the continental shelf, in shallow waters (30 meters depth). It has a net surface of around 2,500 m2 of research capacity, space for laboratories, instrumented containers and capacity to accommodate researchers distributed in a multi-story building with a main dock of 1,000 m2
WAVEC

WavEC provides professionnals with professional engineering services and RDI support in the marine renewable energy sector and related areas.
With a multidisciplinary team they have been expanding our competences to offshore aquaculture and other ocean engineering solutions.
SWANSEA Univ

MAREI
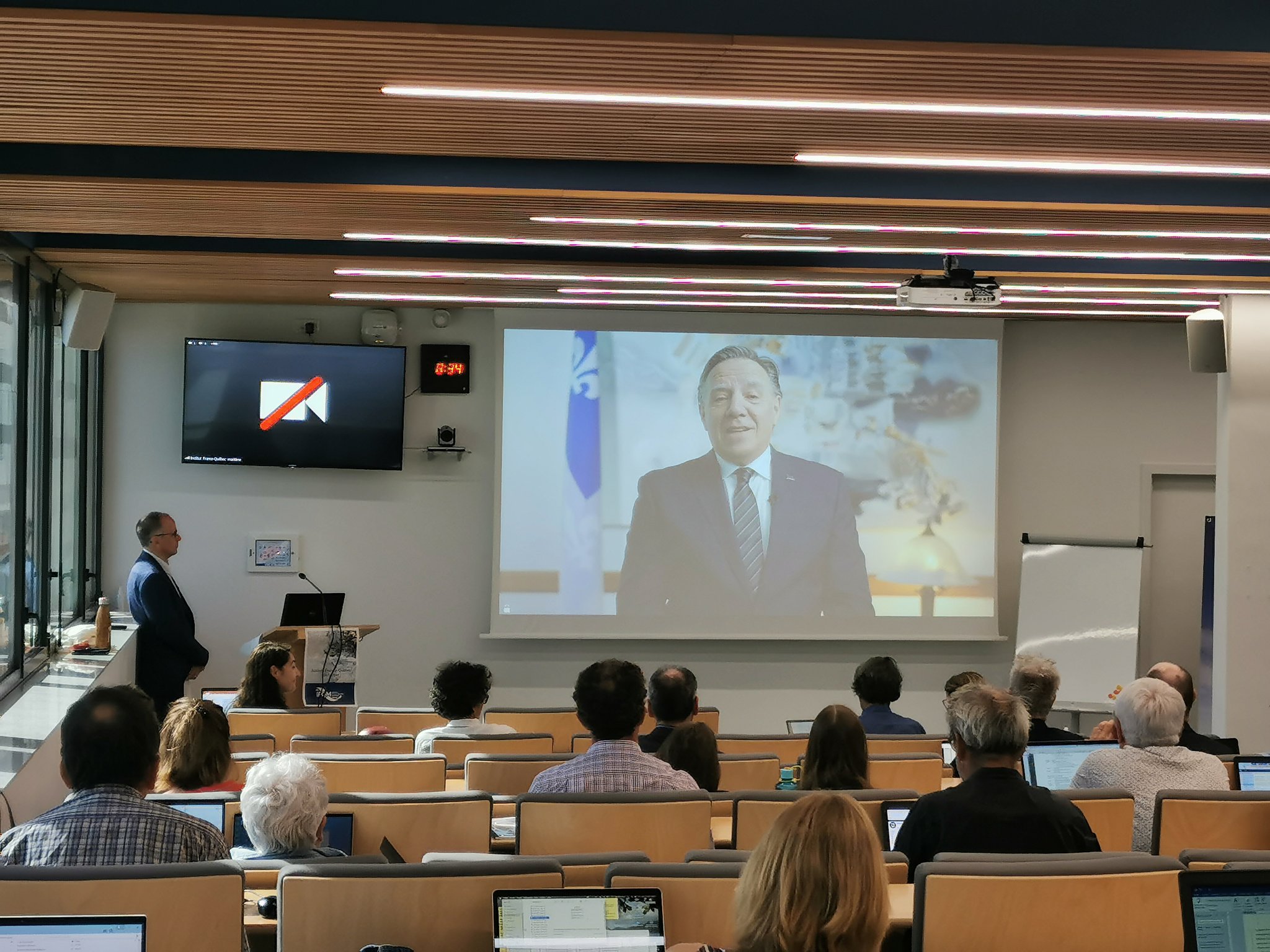


During this second edition, the goals were both to capitalize on the first four years, but also a forward-looking approach, in order to mobilize the economic sector by promoting bridges with research and innovation in marine sciences. These two days of work were centered on two key moments:
- a collaborative work within different thematic workshops to define the new strategy of the coming mandate (2022-2026).
- a work of linking and exchanging with the economic world thanks to the support of historical partners such as the Pôle Mer Bretagne Atlantique. The dynamic local ecosystem (Loire-Atlantique, Nantes and St-Nazaire) in the maritime fields was also an asset. This was particularly the case with visits to companies and network heads, which helped create the conditions for partnerships and transfers between the world of research and innovation and the industrial world in France and Quebec.
Conducted by : ECN (LHEEA),
Animated by : WEAMEC
Others partners : IUML, Nantes University (GeM , IREENA)

The objective of the of the network is to encourage cross-sector and cross-regional collaborations between SMEs and associated members (research organizations, large companies, in the field of renewable energy, large companies, institutions) in the field of MREs.
WEAMEC is one of the partners in this project which includes Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (coordinator), DMEC (Netherlands), Scottish Enterprise (UK), Offshore Renewable Energy Catapult (UK), Sirris (Belgium) and Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung (Germany). Our partner, the EMC2 cluster, helped to put us in touch with the consortium to set up the project.
Conducted by Nantes Université, at the LEMNA laboratory, by Lionel LEMIALE.
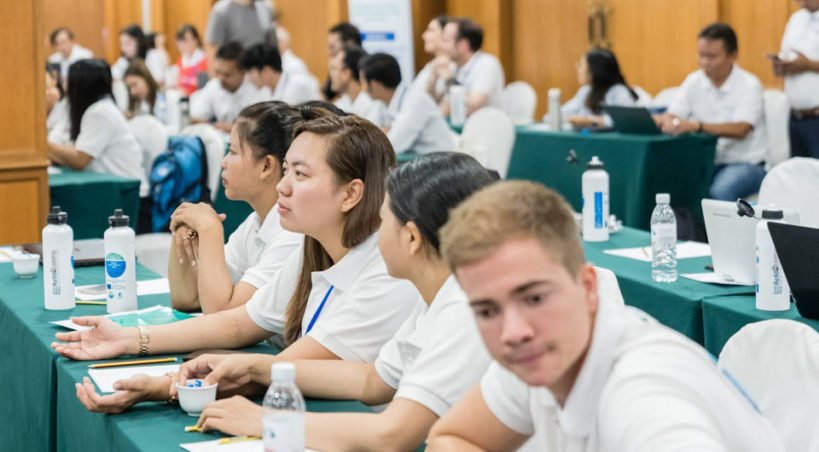 WANASEA (« Strenghten the Production, Management and Outreach Capacities of Research in the Field of WAter and NAtural Resources in South-Est Asia ») is a structural project cofounded by the Erasmus + program – KA2 Cooperation for innovation and exchange of good practices – Capacity Building in the field of Higher Education. The consortium includes 6 European partners (France, Denmark, Spain) and 9 south-East Asian partners (Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand).
WANASEA (« Strenghten the Production, Management and Outreach Capacities of Research in the Field of WAter and NAtural Resources in South-Est Asia ») is a structural project cofounded by the Erasmus + program – KA2 Cooperation for innovation and exchange of good practices – Capacity Building in the field of Higher Education. The consortium includes 6 European partners (France, Denmark, Spain) and 9 south-East Asian partners (Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand).
The WANASEA project aims at building capacity in the field of higher education in the south-east Asian partner countries. The project aims at providing training, research and networking sessions focused on water and its associated natural resources, considered as a major contemporary challenge.
Objectives and activities
The objective of the project is to improve the quality of study programs and build capacity in the field of research for south-East Asian higher education institutions in the field of water and natural resources. It stands for a multidisciplinary process which favors the academic openness towards social and economic stakeholders.
The activities of the project focused on an analysis of the existing academic curriculum in south-East Asian partner institutions as well as of their expectations. From this analysis, the project will implement:
- a set of training sessions for the university staff members, which will be organized twice a year
- a platform to enhance the exchange and transfer of knowledge and methodological tools, which will be used by young researchers.
Projet IRP Initiative NExT-Research and international
Project from 2018 to 2021
Conducted by : GEPEA
Partners : UN, IMT Atlantique, Ifsttar, CNRS (GEPEA, l’Institut des Matériaux Jean Rouxel, le Laboratoire Espaces et Sociétés, le Laboratoire de Psychologie des Pays de la Loire, GPEMn (IFSTTAR)), UCLA (Université de Californie à Los Angeles)
The DISCUS project aims to develop innovative solutions to the challenges of sustainable development in ultra-urban areas, by
 optimizing the links between food, energy and water. To do this, DISCUS brings together teams based in Nantes and Los Angeles (UCLA). Both cities are located near an ocean (Pacific or Atlantic), with important industrial and commercial activities (aerospace, energy, for example) and commercial ports (San Pedro / Long Beach and Saint Nazaire). They have similar population densities ranging from 3,000 (Los Angeles) to 4,500 (Nantes) people/km2. Both are also home to strong and well established academic activity. Through this international collaboration, the challenges and opportunities that exist in each of these countries, with different urban scales, regulatory frameworks, and economic and entrepreneurial ecosystems, can be compared. This will provide the framework for studies to propose and develop solutions that can be used and adapted to various urban environments. Implementing solutions to the challenges of sustainable development in urban centers is inherently multidisciplinary.
optimizing the links between food, energy and water. To do this, DISCUS brings together teams based in Nantes and Los Angeles (UCLA). Both cities are located near an ocean (Pacific or Atlantic), with important industrial and commercial activities (aerospace, energy, for example) and commercial ports (San Pedro / Long Beach and Saint Nazaire). They have similar population densities ranging from 3,000 (Los Angeles) to 4,500 (Nantes) people/km2. Both are also home to strong and well established academic activity. Through this international collaboration, the challenges and opportunities that exist in each of these countries, with different urban scales, regulatory frameworks, and economic and entrepreneurial ecosystems, can be compared. This will provide the framework for studies to propose and develop solutions that can be used and adapted to various urban environments. Implementing solutions to the challenges of sustainable development in urban centers is inherently multidisciplinary.The challenges are :
- technological and scientific to develop innovative and environmentally friendly solutions that can be deployed at the scale of a building, an entire neighborhood and a metropolis;
- societal and behavioral because their deployment will require acceptability and changes in practices on the part of individuals and communities;
- economic because the successful deployment of the solutions developed and the necessary transformation of communities can only be achieved if they are financially viable for all stakeholders.
OCEANEXT is a multidisciplinary international conference, initiated in 2016 by the COSELMAR program. Organized by the Institut Universitaire Mer et Littoral (IUML, FR3473), each session of OCEANEXT takes place on a theme and brings together international scientists.
Some figures of the 2026 edition:
More than 220 registrants, researchers representing laboratories of 18 different nationalities (Belgium, Canada, Chile, Finland, France, Germany, Ghana, Ireland, Morocco, New Caledonia, Netherlands, Norway, New Zealand, Portugal, South Africa, Spain, USA), 4 plenary sessions, 14 keynotes, 65 oral presentations, 19 flash presentations, 20 posters, 4 roundtables and 9 pairs for "3 minutes for COSELMAR"!
To learn more about this event >>>Conducted by : universities in Cambodia: National University of Management (NUM); Royal University of Law and Economics (RULE); University of Battambang (UBB); Royal University of Agriculture (RUA). An important institutional support is provided by the Ministry of Education Youth and Sport.
Partners : Université de Nantes (France), Universidade de Vigo (Spain) and Syddansk Universitet (Denmark)
Cofinanced by Erasmus + Programme
DOCtoral program in Khmer universities Strengthening the International Development of Environmental and maritime research (DOCKSIDE) is a structural project co-funded
 by Erasmus + programme, KA2 Cooperation for innovation and exchange of good practices – Capacity Building in the field of Higher Education.
by Erasmus + programme, KA2 Cooperation for innovation and exchange of good practices – Capacity Building in the field of Higher Education.Objectives
- Strengthen the collaboration between Cambodian and European universities
- Improve the quality and attractiveness of PhD programs in Cambodia
- Scientific cooperation between researchers and PhD students
- Development of multidisciplinary research
- A more international Cambodian and European university
Project from 2014 to 2019
Conducted by : CDMO, LEMNA, LETG
 The project deals with the notional rethinking of maritime law. The development of human activities on the sea environment leads to a transformation of the law of the sea and maritime law. The law has the function of civilizing the new activities that technological innovations allow.
The project deals with the notional rethinking of maritime law. The development of human activities on the sea environment leads to a transformation of the law of the sea and maritime law. The law has the function of civilizing the new activities that technological innovations allow.Extraction activities on the continental shelf were taken into account by the Geneva Convention of 1958, then the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea of 1982, in order to protect coastal States.
The creation of the Exclusive Economic Zone, by the 1982 Convention, seeks to control fishing effort and protect fishery resources.
However, maritime law remains centered on the concept of the vessel, leaving aside the new seagoing vessels and their workers. The development of illicit activities at sea calls into question the competences of States, as well as their cooperation.
Maritime transport has been a laboratory of globalization since the 1970s through the open registration of ships. The attachment of the ship to the State had to be supplemented by the controls of the port States and the development of a minimum international law, created by the IMO and the ILO. However, the internationalization of maritime labor leaves room for a mosaic of national legislations, i.e. a poorly regulated competition. In addition to ships, seamen and seafarers, the status of exploration or exploitation platforms, inspired by mining law, leaves large areas of uncertainty as to the status of their workers, which the coastal State cannot fill, particularly given the diversity of operators and exploiters, who are likely to freely choose their headquarters and the law applicable to employment contracts.
The development of human activities at sea requires a rethinking of the concepts born from the history of maritime activities and navigation. The development of illicit activities at sea calls into question the intervention of States, from their territorial waters to the ocean. The compromises reached in 1982 deserve to be questioned, taking into account new threats and techniques. How can we think in the 21st century about the civilization of these new activities at sea through the Law?
Conducted by :ECN (LHEEA) - GeM : Co-supervisor ESR#7 FP7 ITN OCEANET 2013-2017
 OceanNET is a multinational Initial Training Network (ITN) funded under the PEOPLE Programme (Marie Curie Actions) of European Union’s FP7. The aim of the network is to train 13 Early Stage Researcher (ESR) in the area of floating offshore wind and wave energies to support the emerging marine renewable energy sector.
OceanNET is a multinational Initial Training Network (ITN) funded under the PEOPLE Programme (Marie Curie Actions) of European Union’s FP7. The aim of the network is to train 13 Early Stage Researcher (ESR) in the area of floating offshore wind and wave energies to support the emerging marine renewable energy sector.OceaNET concerned the development of four innovative products for offshore wind and wave energy farms :
- namely an environmental monitoring hardware and software package,
- underwater electrical connectors and associated ROVs,
- air turbine for oscillating water column (OWC) wave energy converters and
- an O&M support software package.














